Fc Effector Activity Bioassays
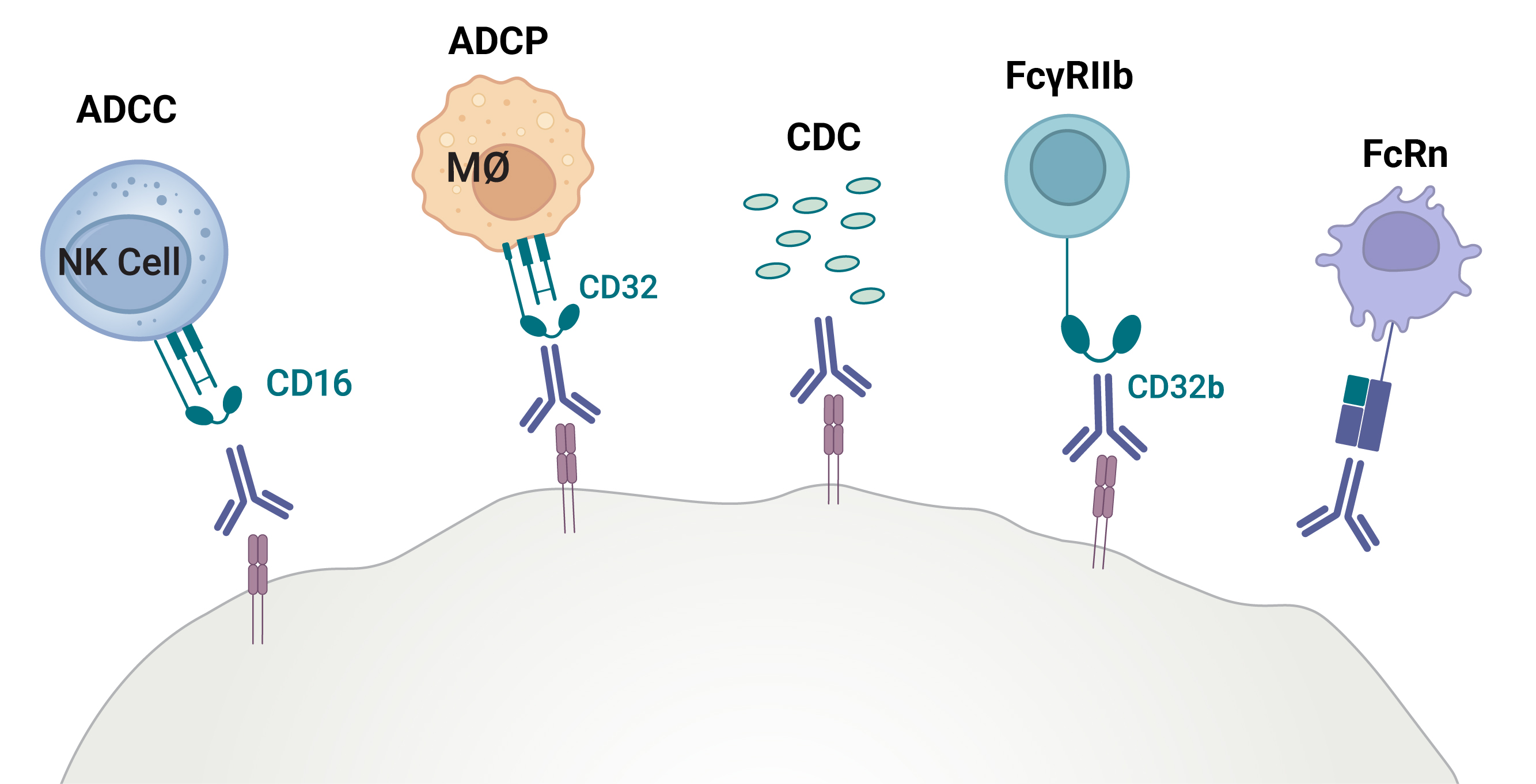
Monoclonal antibody therapeutics have revolutionized the treatment of a wide range of cancer and autoimmune disorders. These immunomodulatory molecules effector mechanism depends heavily on its Fc region and specifically, how well that region engages Fc receptors, such as FcRn and FcγRs on immune cells. Mechanisms like antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) are vital to clinical success, yet difficult to measure in a comprehensive manner.
Promega has developed a broad suite of bioluminescent tools that enable biologic drug developers to assess their antibody therapeutic Fc effector function from lead generation through lot release.
What Are Fc Effector Activity Assays?
Fc effector activity assays are designed to measure antibody functional activity through Fc receptor engagement. They have several important immune mechanisms:
- ADCC (Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity)
- ADCP (Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis)
- CDC (Complement-dependent cytotoxicity)
- FcRn (Neonatal Fc Receptor)
Are you looking for greater confidence and simplicity in your Fc effector characterization?
Whether you’re developing a novel antibody or ensuring biosimilar comparability, you need greater control and confidence in Fc analytics. From early antibody discovery through IND, BLA, and lot release you deserve:
- Time savings by eliminating cumbersome and labor-intensive protocols
- Assay platforms that are scalable, sensitive, and easy to use
- Accurate, decision-ready data that meets regulatory guidelines
Promega Fc effector assays provide a comprehensive workflow designed to deliver exactly that:
- Biochemical precision with Lumit® Binding Assays
- Robust, ICH qualified Reporter Bioassays
- Physiological Relevant Cytotoxicity HiBiT Target Cell Killing Bioassays
Measure Every Mechanism With A Complete Fc Effector Characterization
Comprehensive assay continuum from binding to bridging – An integrated suite of Lumit® FcγR binding, Fc Effector Reporter, and HiBiT Target Cell Killing (TCK) assays provides a coherent workflow that tracks an antibody’s Fc effector activity from initial screening through lot release
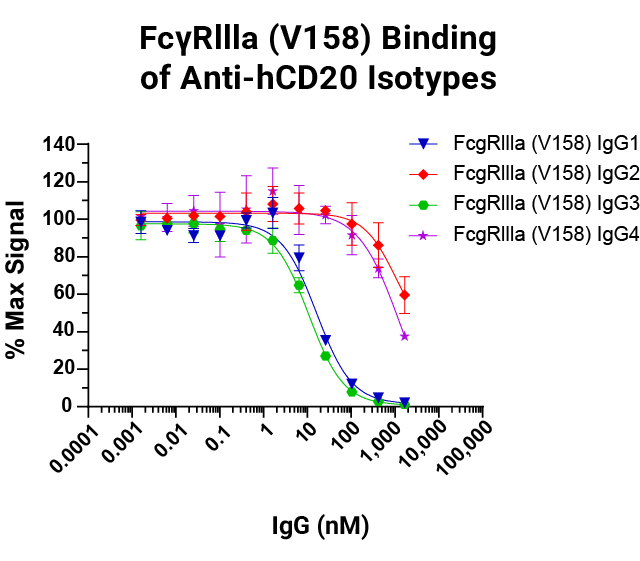
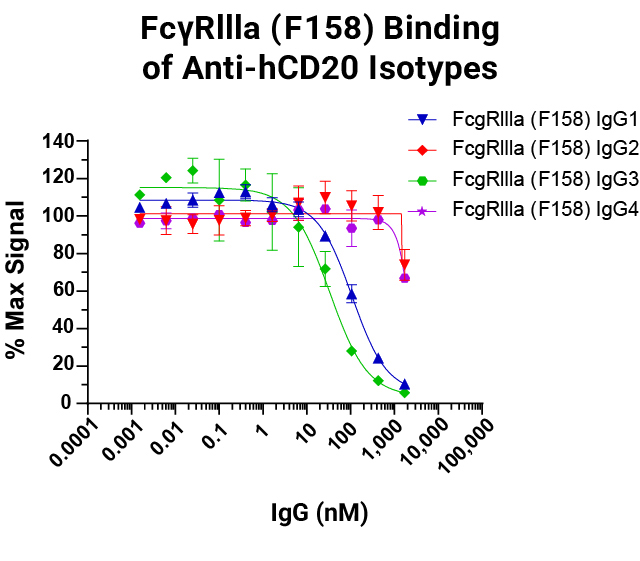
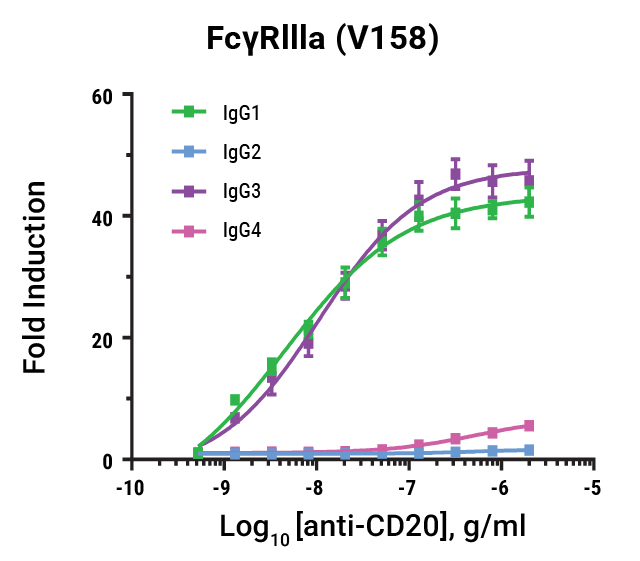
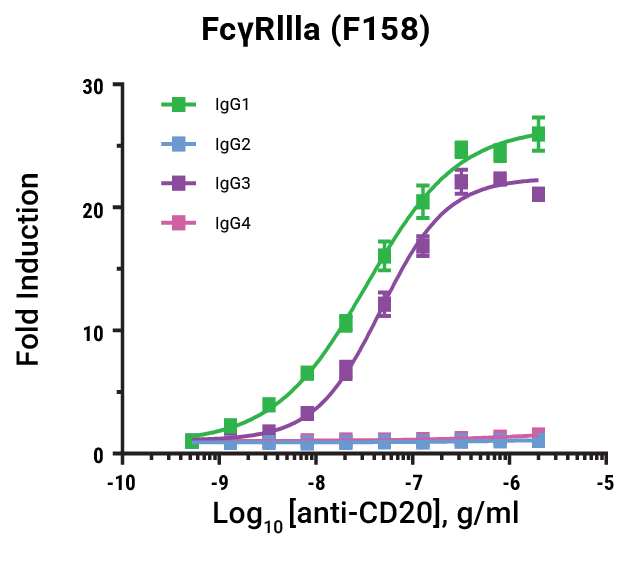
Lumit® FcγR Binding Immunoassays
are suitable for rank ordering different IgG subclasses based on their affinity to the different allelic variants for ADCC and ADCP function. Data shown for FcγRIIIa V158 and F158.
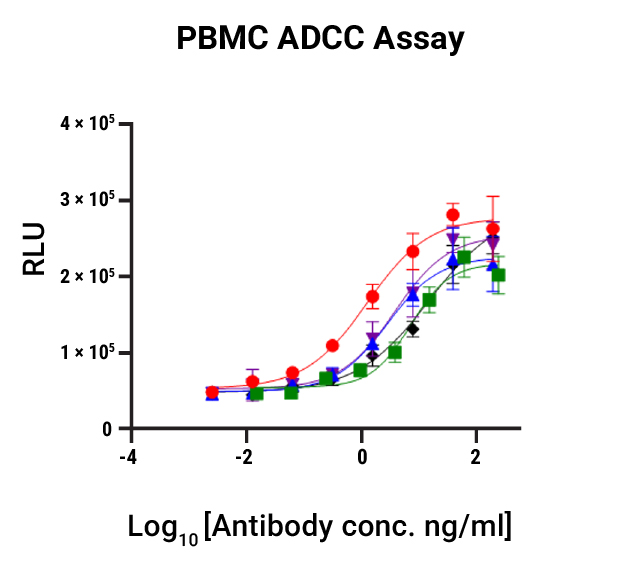
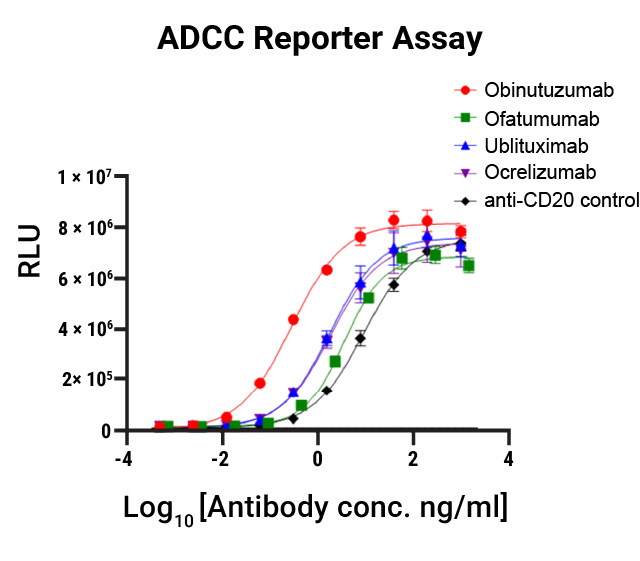
Fc Effector Activity Assays for Antibody Therapeutics
 ADCC
ADCC
FcγRIII
- Human ADCC (V158/F158)
- Lumit® FcγRIIIa (V158/F158)
- Cyno FcγRIII ADCC
- Mouse FcγRIII ADCC Bioassay
- Canine FcγRIII ADCC
FcγRIV
Multiple FcRs
 ADCP
ADCP
FcγRIIa
- Human ADCP Bioassay (R131/H131)
- Cyno FcγRIIa ADCP Bioassay
- Lumit® FcγRIIa (R131/H131)
Multiple FcRs
 CDC
CDC
 FcRn
FcRn
 FcyRIIb
FcyRIIb
Comparative Workflow Snapshots
| Feature | Lumit® Immunoassays | Reporter Bioassay | HiBiT TCK Bioassays |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assay Format | Biochemical Binding | Cell-based, Functional Reporter | Primary Effector Cells Paired with Target Cells |
| Throughput / Scalability | 96- or 384-well | 96 or 384-well | 96-well |
| Time-to-Result | Fast: 60 minutes | Short: 6 hours | Flexible: 6–24 hours |
| Data Type | Screening and Rank Order Binding | Potency and Functional MoA | Cell Lysis and Cytotoxicity |
| Development Phase | Early Discovery, Lead Generation and Optimization | Preclinical, QC/Lot Release in cGMP environments | Bridging Studies |
| Instrumentation | Standard Luminometer | Standard Luminometer | Standard Luminometer |
Featured Publications
| Study Title | Application | Promega Assay Role |
|---|---|---|
| A homogeneous bioluminescent immunoassay for parallel characterization of binding between a panel of antibodies and a family of Fcγ receptors (Sci. Rep., 2022) | Rank-ordering antibody and FcyR interactions | Cell-based, functional reporter |
| FCGR2A-HH Gene Variants Encoding the Fc Gamma Receptor for the C-Reactive Protein Are Associated with Enhanced Monocyte CD32 Expression and Cardiovascular Events’ Recurrence after Primary Acute Coronary Syndrome (Biomedicines, 2022) | Inflammation biomarker characterization | ADCP Reporter Bioassays to quantify bioactivity |
| An Engineered Oncolytic Virus Expressing PD-L1 Inhibitors Activates Tumor Neoantigen-Specific T Cell Responses (Nat. Comm., 2020) | Immunotherapy validation | Validated Fc-mediated enhancement of ADCC activity. |
| A Citrullinated Histone H3 mAb for Immune Modulation in Sepsis (Nat. Comm., 2025) | mAb safety screening | Showed absence of FcγR activation, supporting safety claims. |
| The newly engineered monoclonal antibody ON104, targeting the oxidized Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (oxMIF), ameliorates clinical and histopathological signs of collagen-induced arthritis (Eur. J. Immun., 2023) | Antibody engineering | HiBiT Target Cell Killing measuring CDC activity |
Do you know how well your antibody is internalized?
We offer a cell-based assay to measure antibody internalization without the need for pH dependent dyes
Learn more about the Antibody Internalization Assay
Frequently Asked Questions
Measuring Fc Effector Functions:
How do I measure effector activity of the antibody Fc region?
Measure Fc effector activity with a tiered approach: begin with biochemical immunoassays to confirm engagement of FcγR, C1q, and, when relevant, FcRn. Next, run cell-based functional assays for ADCC. ADCP, and CDC to determine relative potency. Finally, confirm orthogonally with a primary cell assay as a bridging method to support your data.
Measuring Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC):
How do I measure ADCC activity?
Measure ADCC by co-culturing antigen-positive target cells and effector cells expressing FcγRIIIa (V158/F158). Use either (a) reporter bioassays that measure FcγRIIIa signaling or (b) primary-cell killing assays that quantify target lysis (e.g., HiBiT Target Cell Killing Bioassays).
Measuring Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP):
How do I measure ADCP activity?
Measure ADCP by co-culturing antigen-positive target cells and effector cells expressing FcγRIIa alleles (H131/R131). Use either (a) reporter bioassays that measure FcγRIIa signaling or (b) primary-cell killing assays that quantify target lysis via phagocytosis (e.g., HiBiT Target Cell Killing Bioassays).
Measuring Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC):
How do I measure CDC activity?
Use the Lumit® C1q Binding Assay as a surrogate measure CDC and detect complement engagement across antibody isotypes and engineered variants; it’s useful for biosimilar comparability and Fc engineering programs.