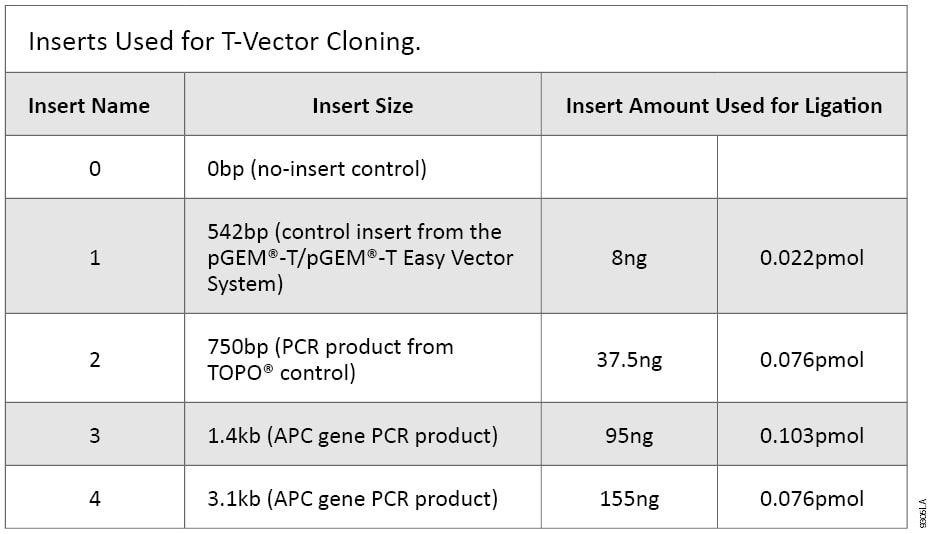
Comparing Cloning Efficiency of the pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vectors to the TOPO TA Cloning® Vectors
Lynn Litterer
Promega Corporation
Publication Date: 2009
Abstract
We evaluated the cloning efficiency of different size PCR products into three T-vector cloning systems. The pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vector Systems gave a high number of recombinants across a broad range of insert sizes (0.5–3 kb) while the TOPO TA Cloning® system worked well for inserts less than 1 kb, but showed a striking decrease in performance with larger insert sizes (1–3 kb).
Introduction
Many DNA sequence manipulations are made easier by cloning a PCR product into an appropriate vector. This allows large-scale replication of DNA in bacteria, DNA sequence confirmation and addition of restriction endonuclease sites for easy subcloning of the target DNA. Standard PCR with Taq DNA polymerase produces PCR products with a single deoxyadenosine overhang at each 3′ end. These single-nucleotide overhangs anneal to the 3′‑thymidine overhangs of T-cloning vectors such as the Promega pGEM®-T (Cat.# A3600) and pGEM®-T Easy Vectors (Cat.# A1360) and the Invitrogen TOPO® TA Cloning Kit with pCR®2.1-TOPO® Vector (Invitrogen Cat.# K4500-01). Theoretically, smaller inserts will be cloned more efficiently than longer inserts. We tested the effect of PCR product length using three T-cloning systems. PCR cloning efficiency was determined using PCR products ranging from 542 to 3,100 base pairs with the pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vectors and pCR®2.1-TOPO® Vector.
Methods
Four different inserts were amplified and cloned into the pGEM®-T, pGEM®-T Easy and TOPO® TA Vectors. Inserts 2, 3 and 4 were amplified using GoTaq® DNA Polymerase. Insert 2 used PCR buffers and components from the TOPO® kit and was amplified with 1 µl (5 units) of GoTaq® DNA Polymerase in a 100 µl reaction for 25 cycles. Inserts 3 and 4 were amplified as previously described (1). PCR products were then purified using Wizard® SV Gel and PCR Clean-Up System (Cat.# A9281). Purified inserts were quantified by absorbance at 260 nm on a NanoDrop® Spectrophotometer. Concentration and insert purity were confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1).
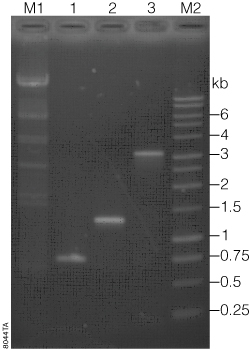
Lane M1, Lambda DNA/HindIII Markers (Cat.# G1711); Lane 1, Insert 2 (542 bp); Lane 2, Insert 3 (1.4 kb APC); Lane 3, Insert 4 (3.1 kb APC); Lane M2, 1 kb DNA Ladder (Cat.# G5711).
Ligations and transformations were performed as directed by the manufacturer with minor modifications. The pGEM®-T ligations were increased to 12 µl final volume to allow for a larger volume of insert. The same amount of insert was used for every ligation regardless of TA vector used. An insert-to-vector ratio between 3:1 and 1:3 is recommended for the pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vector Systems. We chose the higher insert-to-vector ratio (3:1) to improve the recovery of clones with long inserts. The TOPO TA Cloning® Kit does not give a recommended insert amount to use, so identical amounts of insert were used in both systems. Ligations and transformations were performed in duplicate on different days using the same DNA samples. For pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vectors, ligations were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes; for the pCR®2.1-TOPO® Vector, ligation reactions were incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. Ligations were stored at –20 °C, then thawed on ice just before transformation.
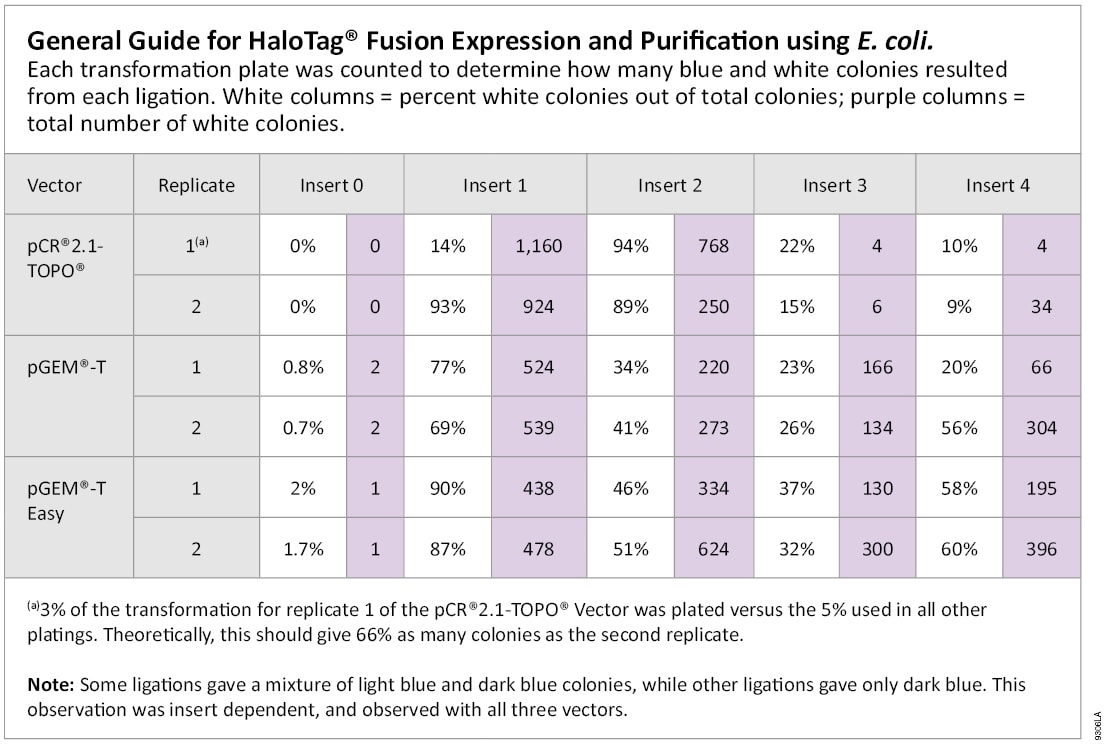
Transformation reactions were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. TOPO® TA reactions were transformed into TOP10 chemically competent cells, and pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vector reactions were transformed into JM109 Competent Cells (Cat.# L2001). Two microliters from each reaction was transformed and 5% of the transformation plated on LB plates containing 100 µg/ml ampicillin, 80 µg/ml X-Gal, 0.5 mM IPTG or LB plates containing 50 µg/ml kanamycin with 1.6 mg X-gal spread on the surface (32 µl of 50 mg/ml X-Gal [Cat.# V3941]) for blue/white selection. Plates were scored for blue and white colonies with the number of blue colonies including both dark and light blue colonies.
Results
All systems tested gave large numbers of colonies when ligating short inserts (<1 kb; Table 2). With longer inserts (>1 kb), the pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vector systems give many more white colonies than the TOPO® TA system, suggesting more efficient ligation. The TOPO® manual indicates that any PCR product greater than 1 kb should be considered a “long” insert.
Conclusions
All T-vector cloning systems tested worked well for short inserts (<1 kb), giving hundreds of recombinant colonies as indicated by blue/white selection. The TOPO TA Cloning® Kit gave a higher percentage of white colonies for this insert size. For larger inserts (1–3 kb), the pGEM-T® and pGEM®-T Easy Vector Systems yielded significantly more recombinant colonies with a greater percentage of white colonies than the TOPO TA Cloning® system. We conclude the pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vectors are a better choice for cloning a broader range of insert sizes especially in the commonly used 1–3 kb range. (1)
References
- Knoche, K. et al. (2005) GoTaq® Flexi DNA Polymerase: Robust performance with magnesium optimization. Promega Notes 89, 17–20.
Learn more about the pGEM®-T Vector Systems