Wastewater Surveillance for Tracking COVID-19 and Other Diseases
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE), or sewershed surveillance, is the analysis of wastewater to identify the presence of biologicals or chemicals for the purpose of monitoring public health. WBE has previously been used to detect the presence of pharmaceutical or industrial waste, drugs, viruses and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. WBE has proved to be a useful tool for tracking outbreaks and disease dynamics during the COVID-19 pandemic. This strategy shows similar potential in helping public health departments monitor other diseases, including those caused by enteroviruses (such as polio), orthopox viruses (such as monkeypox), as well as emerging pathogen threats in communities around the world.
Our workflow, featuring viral concentration and purification kits along with PCR detection kits, allows you to get wastewater surveillance data in one day!
- <4 hour workflow
- Easy to implement
- Built-in controls
Featured Content: Solutions for Wastewater Disease Surveillance eBook
New to wastewater analysis, or looking for improved methodologies to upgrade your workflow? Our Solutions for Wastewater Disease Surveillance eBook offers background, resources, case studies and more, with plenty of tips to help you conduct wastewater analysis effectively and efficiently.

See how possibilities for screening wastewater expand for Monkeypox and Poliomyelitis
Faster Protocol for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater
Current methods for detecting SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA require separate viral concentration and RNA extraction steps, which can take >8 hours to complete and may not generate consistent results. We developed a unique direct capture method that combines virus concentration, extraction and RNA clean-up steps to greatly reduce sample processing time.
No matter your sample number, we have a method that fits your needs. Our protocol combines vacuum-based direct capture with RNA purification using either mini spin columns, benchtop automation using Maxwell® Instruments, or 96-well plate-based automation.
Our SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Kit for Wastewater includes PPMoV internal process controls and standards to ensure accurate quantification. Choose a single target (N1, N2 or E) or all three.
SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Kit for Wastewater
Wastewater Disease Surveillance Products
Viral DNA and RNA Extraction
The following Maxwell® nucleic acid purification kits are recommended for extracting viral RNA from wastewater samples. These kits used with Maxwell® Instruments allow automated viral RNA extraction from wastewater at up to 48 samples per run.
| Cat.# | Name | Concentration Method | Input Sample Volume | Intended Throughput | Size | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2991 | Wizard® Enviro TNA Kit | Vacuum-Based | 40ml | <16 | 25 preps | Manual Spin Column |
| AS1831 | Maxwell® RSC Enviro TNA Kit | Vacuum-Based | 40ml | 1–48 | 48 preps | Semi-Automated |
| CS347901 | Maxwell® RSC Enviro Nanotrap® A TNA Kit | Ceres Nanotrap® Microbiome A particles | 10ml | >48 | 48 preps | Semi-Automated |
| CS344301 | Maxwell® HT Enviro Nanotrap® A TNA Kit | Ceres Nanotrap® Microbiome A particles | 10ml | >48 | 4 × 96 preps | High-Throughput |
Choose a Format for Your Sample Throughput
Manual: Vacuum + Spin Column
The Wizard® Enviro Total Nucleic Acid Kit (A2991) allows you to get purified TNA in 90 minutes or less with a simple protocol. First, the TNA is directly captured from wastewater using the PureYield™ Midicolumn and Vac-Man® Laboratory Vacuum Manifold. Then, the lysate is further cleaned using PureYield™ Minicolumns. The recommended protocol starts from 40ml of wastewater and results in 40µl of TNA.
Maxwell® Automation: Vacuum + Maxwell® Extraction
The Maxwell® RSC Enviro Total Nucleic Acid Kit (AS1831) allows you to get purified TNA in 2 hours with vacuum-based direct capture of TNA followed by automated TNA extraction using Maxwell® Instruments. The Maxwell® RSC Instrument can process 1 to 16 samples, and the Maxwell® RSC 48 Instrument can process 1 to 48 samples in a single run. Viral TNA is first captured from wastewater using the PureYield™ Midicolumn and Vac-Man® Laboratory Vacuum Manifold. Then, the lysate is loaded into the Maxwell® RSC Instrument for walkaway RNA extraction. The recommended protocol starts from 40ml of wastewater and results in 40µl of TNA.

High-Throughput Concentration and Extraction: Plate-Based
The Maxwell® HT Enviro Concentration and TNA Extraction Kit (CS344301) provides magnetic particle-based concentration of virus with Ceres Nanotrap® particles from 10ml of wastewater followed by extraction of TNA from the concentrate. The reagents are formatted for use with laboratory automation for walkaway sample processing with minimal user intervention. Our Field Support Scientists can help you implement or optimize automation of viral RNA extraction methods that meets your specific needs. Please contact us for more information.

Purification scale-up and automation support
Our Field Support Scientists are available to help you implement or optimize automation of viral RNA extraction methods, regardless of the instrumentation platform used. We’ll help you develop a workflow that meets your specific needs!
Amplification of Wastewater DNA/RNA Targets
PCR reagents, including qPCR and RT-qPCR products, are routinely used to detect and amplify target viral sequences. The SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Kit for Wastewater was developed to detect SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in wastewater and includes multiple controls for internal amplification and inhibitor assessment.
Automated Total Nucleic Acid Purification from Wastewater for Mpox Detection
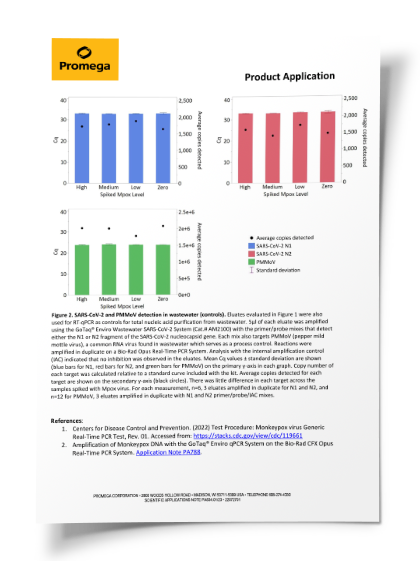
| Cat.# | Name | Reactions/Kit | Gene(s) | Quant Standard | Process & Normalization Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM2100 | GoTaq® Enviro Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 System, N1/N2/E | 200 | N1, N2 or E | N&E and PMMoV RNA | IAC & PMMoV |
| AM2110 | GoTaq® Enviro Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 System, N1 | 200 | N1 | N&E and PMMoV RNA | IAC & PMMoV |
| AM2120 | GoTaq® Enviro Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 System, N2 | 200 | N2 | N&E and PMMoV RNA | IAC & PMMoV |
| AM2130 | GoTaq® Enviro Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 System, E | 200 | E | N&E and PMMoV RNA | IAC & PMMoV |
| CS3174B02 | SARS-CoV-2 Variant Panel- 8 Targets | 8 × 50 preps | 8 sites on S | None | |
| AM2140 | GoTaq® Enviro PMMoV Quant Kit, Quasar® 670 | 100 | PMMoV | PMMoV RNA | |
| CS317417 | MS2 RT-qPCR Kit | 100 | MS2 | MS2 DNA | |
| AM2070 | PMMoV RNA | 100µl | |||
| AM2050 | SARS-CoV-2 (N+E) RNA | 100µl | |||
| AM2060 | SARS-CoV-2 (N+E) dsDNA | 100µl |
Start-Up Kits
The equipment to perform direct capture in your lab.
| Cat.# | Start-Up Kits |
|---|---|
| A3050 | Wizard® Enviro Start-Up Kit, 110V |
| A3060 | Wizard® Enviro Start-Up Kit, 220V |
| A3070 | Maxwell® RSC Enviro Kit Start-Up Kit, 110V |
| A3080 | Maxwell® RSC Enviro Kit Start Up Kit, 220V |
Included with each start-up kit:
- One Reagent Kit (either A2991 for Wizard® Enviro TNA Kit or AS1831 for Maxwell® RSC Enviro TNA Kit)
- Eluator™ Vacuum Elution Device
- Welch Vacuum Pump for North America Electrical
- Vac-Man® Laboratory Vacuum Manifold, 20-sample capacity
- Vac-Man® Jr. Laboratory Vacuum Manifold, #10 Stopper
- 1700ml Flask and Tubing
Advantages of Wastewater Surveillance
Early Warning
SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be detected in human feces a few days to a week before the onset of symptoms. A study showed that sewage surveillance can predict COVID-19 outbreaks even before individual patient testing and hospital admissions.
Population-Wide Data
One wastewater sample can provide data on the average infection rate of thousands of people. This aggregated data can be especially informative to regions with low clinical COVID-19 testing rates.
Low Cost
Instead of individually testing thousands of patients, collecting and testing a small number of wastewater samples is much more cost-efficient for obtaining population-wide data.
Trending Tool
Continual monitoring of wastewater can be used to establish trends in current outbreaks, identify new outbreaks, and prevalence of infections.
Featured Resources
Monkeypox—The Latest Zoonotic Virus Making Headlines
Read about the emerging zoonotic virus monkeypox, and how wastewater surveillance could be used to help researchers track outbreaks.

Disease Dynamics and Wastewater Surveillance in the Las Vegas Desert
Led by Edwin Oh, Ph.D., researchers at the University of Nevada-Las Vegas use wastewater surveillance to track COVID-19 and other emerging pathogens in southern Nevada.

Dr. Claudia Bagutti, State Laboratory of Basel
Dr. Claudia Bagutti, microbiologist and molecular biologist in the State Laboratory of Basel-City, Switzerland, speaks of her own experience leading her lab in WBE, using tools and methods designed at Promega.
Have questions about viral RNA detection in wastewater?
We're happy to answer any questions you may have and work with you to support your needs. Submit the information below to request a free consult and we will be in touch with you shortly!